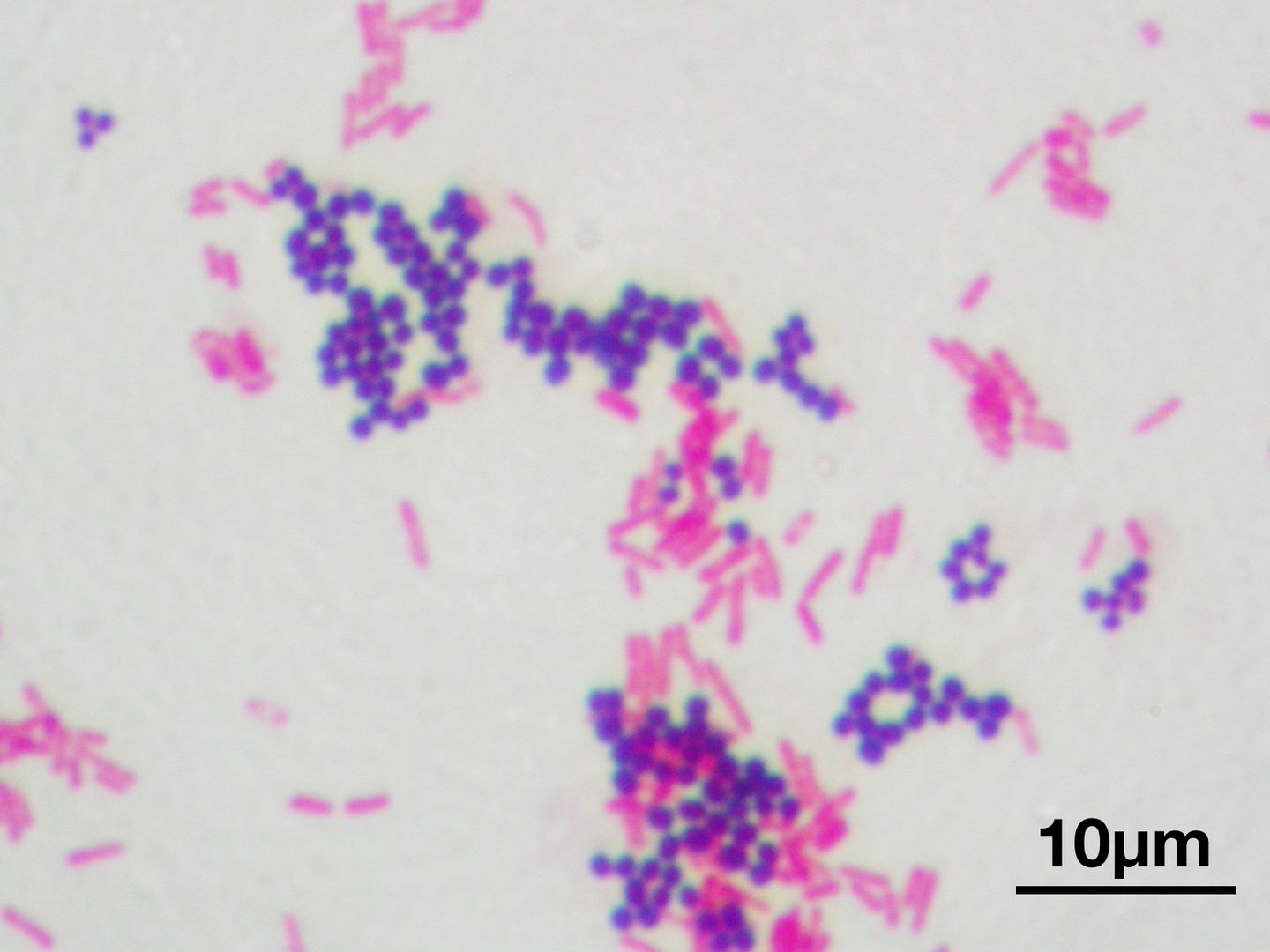
Staining results depend on the types of outer layers
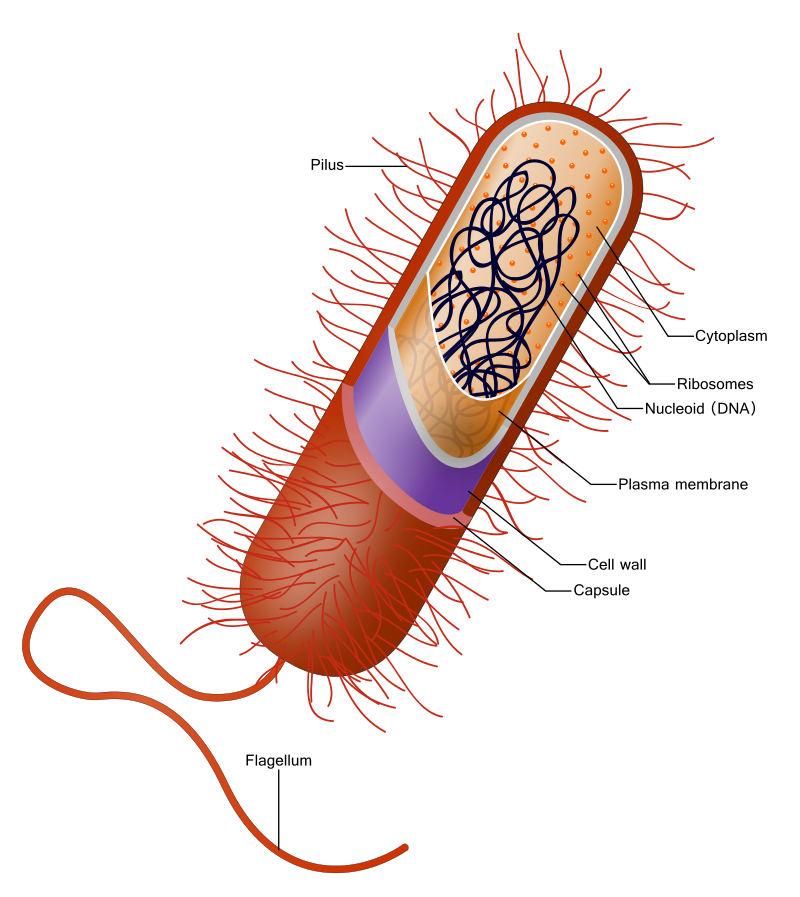
Most bacteria have 3 layers
- Plasma membrane (inner most) — Phospholipid bilayer with some proteins, that directs what enters and exits
- Cell wall (middle) — Peptidoglycan, a polysaccharide, provides structural support
- Capsule (outer) — Sticky layer for attachment and protection.
Differences Between Gram Positive and Gram Negative
Gram Positive
- Inner most plasma membrane (phospholipid bilayer)
- Thick peptidoglycan cell wall
- Outer capsule
- More easily treatable with antibiotics because they do not have the 2nd plasma membrane
- Gram Stain – purple
Gram Negative
- Inner most plasma membrane (phospholipid bilayer)
- Thinner peptdoglycan cell wall
- Additional 2nd outer plasma membrane
- Outer capsule
- Harder to treat with antibiotics because of 2nd plasma memberane
- Gram Stain – red/ pink
Gram Stain Procedure & Result
- Purpose is to help identify the type of bacteria that is making a person sick.
- Treatment would differ based on the results of the identity
- Steps:
- Smear bacteria sample across a glass slide — using an inoculation loop taking from a culture medium to the slide
- Heat fix the bacteria to the slide using an open slide to keep it from washing away
- Apply Crystal Violet to the bacteria on the slide. Particles will pass through the outer layers and into the bacteria’s cell
- Add iodine to the bacteria — brownish gold color will pass through layers, enter the cell and bind with the crystal violet molecules.
- Wash the bacteria with alcohol to shrink and dissolve the outer capsule of both types of bacteria. In the Gram Negative, the outer plasma layer will also be washed away. The difference is that the cell wall is thicker on the Gram Positive bacteria. And with the thinner Gram Negative cell wall, the Crystal Violet/iodine molecules will wash away. The Gram Negative will look transparent.
- Apply Safranin to the bacteria. The red molecules of the Safranin will bind with the remaining molecules of the plasma/phospholipid bilayer.
- Result:
- Gram Positive bacteria will look purple because Crystal Violet is more visible
- Gram Negative will appear pink
Reference